Cancer remains one of the most formidable health challenges of our time, affecting millions of lives worldwide each year. Understanding this complex disease is crucial for prevention, early detection, and effective treatment. In this article, we delve into the intricacies of cancer, covering its causes, symptoms, and methods of diagnosis.

What is Cancer?
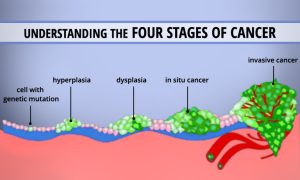
Cancer is a group of diseases characterized by the abnormal growth and spread of cells in the body. These abnormal cells can form tumors, invade nearby tissues, and metastasize to other parts of the body. There are over 100 different types of cancer, each with its own unique characteristics and treatment approaches.
Causes of Cancer
While the exact causes of cancer are multifaceted and often complex, several risk factors have been identified. These include:
- Genetic Factors: Some cancers can be hereditary, meaning they are passed down through generations due to genetic mutations.
- Lifestyle Choices: Factors such as smoking, excessive alcohol consumption, poor diet, and lack of physical activity can increase the risk of developing certain types of cancer.
- Environmental Exposures: Exposure to carcinogens such as radiation, asbestos, and certain chemicals can contribute to the development of cancer.
- Chronic Infections: Certain viruses, bacteria, and parasites have been linked to an increased risk of specific cancers. For example, the human papillomavirus (HPV) is associated with cervical cancer, while Helicobacter pylori infection is a risk factor for stomach cancer.
Symptoms of Cancer
The symptoms of cancer can vary widely depending on the type and location of the disease. However, some common signs and symptoms include:
- Unexplained Weight Loss: Significant and unexplained weight loss can be a symptom of various types of cancer.
- Persistent Fatigue: Cancer-related fatigue is often severe and not relieved by rest.
- Changes in Bowel or Bladder Habits: Persistent changes in bowel or bladder habits, such as blood in the stool or urine, can be indicative of colorectal or bladder cancer.
- Unexplained Pain: Persistent pain that is not related to other conditions should be evaluated by a healthcare professional.
- Changes in Skin: Changes in the size, shape, or color of moles or skin lesions should be examined, as they could be signs of skin cancer.
Diagnosis of Cancer
Early detection plays a crucial role in the successful treatment of cancer. Diagnostic methods vary depending on the type of cancer suspected but may include:
- Imaging Tests: X-rays, CT scans, MRI scans, ultrasound, and PET scans can help detect tumors and determine their size and location.
- Biopsy: A biopsy involves the removal of a small sample of tissue for examination under a microscope to check for cancer cells.
- Blood Tests: Certain cancers can be detected through blood tests that measure specific markers or substances indicative of cancer.
In conclusion, cancer is a complex disease with various causes, symptoms, and diagnostic methods. By understanding these aspects of cancer, individuals can take proactive steps to reduce their risk, recognize potential warning signs, and seek timely medical attention for early detection and treatment.